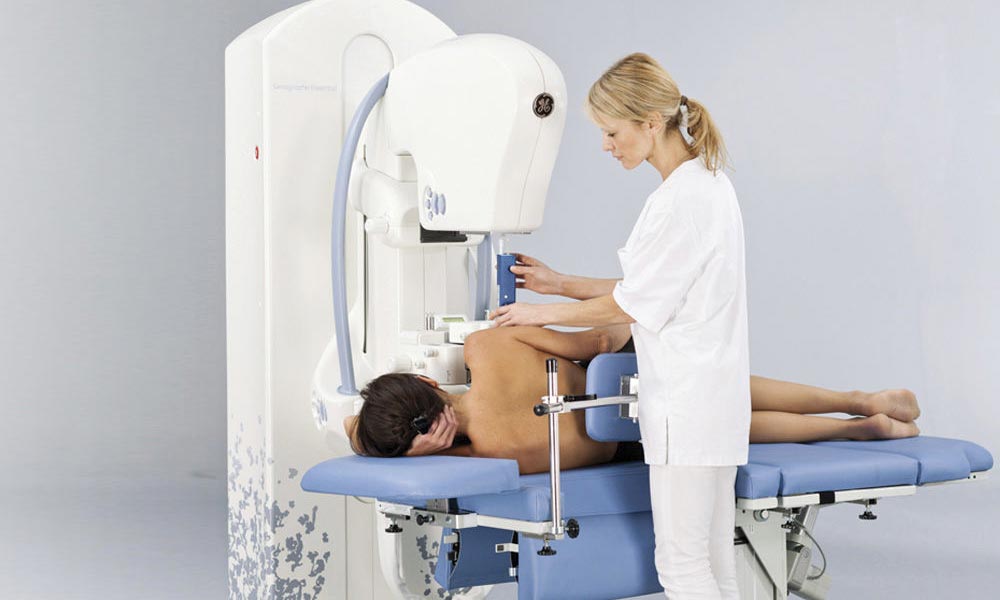
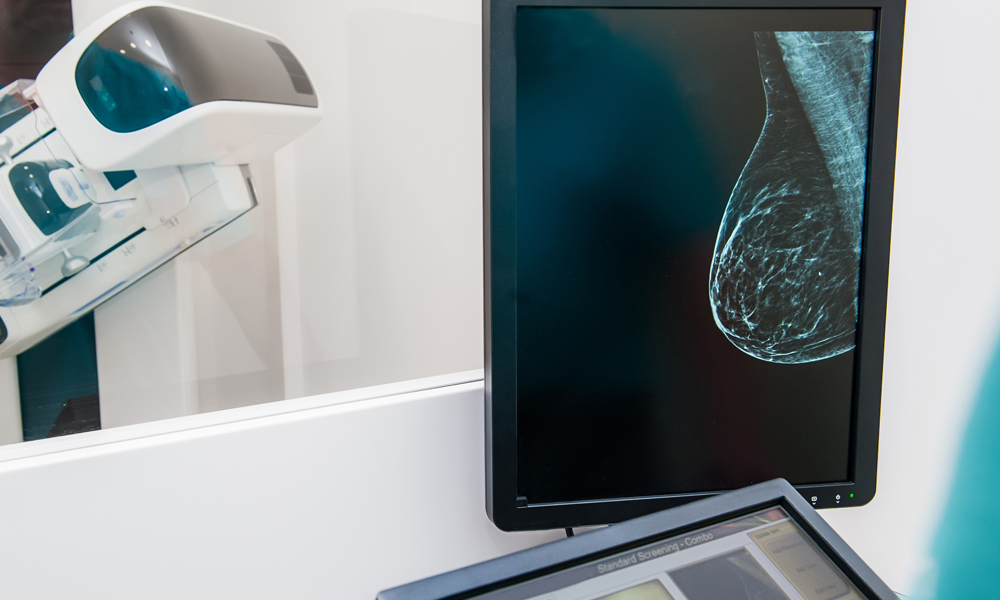
A stereotactic core biopsy (SCB) uses a mammography machine to guide a biopsy needle into an area of concern. When suspicious lesions are identified on a mammogram, but cannot be found with ultrasound or clinical breast exam, a mammogram is used to create the necessary visibility to find the lesion. One of the most common reasons for a SCB is to biopsy microcalcifications, which are flecks of white calcium usually only seen on a mammogram, and almost always missed by clinical breast exam, ultrasound or MRI.
 We’ve been working hard on this. Add your e-mail address and we will tell you as soon as it launches.
We’ve been working hard on this. Add your e-mail address and we will tell you as soon as it launches.
How does it work?
A stereotactic biopsy is usually performed in a radiology suite. You are either seated in a chair or lie on a table (depending on the type of equipment), while your breast is placed between the imaging plates and a mammogram is taken to find the area of suspicion.
Your breast is maneuvered to an opening in a plate which aligns with the target area, while your breast is left softly clamped in position for the rest of the procedure. The radiologist uses Betadine to clean the skin, and injects local anesthesia into your breast skin and tissue to numb the area. Your radiologist then makes a tiny nick, inserts a biopsy needle, and removes a portion of tissue from the suspicious area. The tissue samples themselves are then imaged with a mammogram to confirm removal of the target.
Get discounted Tier 2 tickets while they last. Watch the Summit via on-demand video from anywhere or attend in person at the breathtaking oceanfront Terranea Resort in Southern California.
What happens afterwards?
After all the samples are taken, a titanium clip is deployed to mark the biopsy site (don’t worry, you won’t set off airport security, you can’t feel the clip, and it doesn’t migrate). The clip is important for several reasons:
- To mark the correct spot – small masses can disappear, and if cancer is found, it needs to be completely removed, so the clip confirms the location
- To prove that the mass has already been evaluated – anyone reading your future mammograms will know that this area was biopsied
- To create clarity – if the mass were seen on ultrasound and mammogram, a repeat mammogram after the biopsy will need to show the clip in the right spot – otherwise, it is possible that ultrasound and mammogram actually saw two different things
After the clip is successfully placed, gentle pressure is placed on the breast for about 10 minutes to stop any bleeding on the inside from the biopsy. No stitches are needed – a band aid is placed over the small incision and you can drive home or go back to work immediately afterwards.
Follow Power Up
Follow Power Up
Does it hurt, and for how long?
Most people can have a little discomfort, and you might be sore enough to need some Tylenol or Ibuprofen. Ice helps ease the pain, and an icepack should be offered to you after the biopsy. Exercise or immersing underwater (like in a Jacuzzi or bath) is prohibited for 2 days, but other than that, you can shower and perform usual activities right away.
How accurate is it?
Stereotactic core biopsies take large enough tissue sample so that results are 95-98% accurate.
How soon will I know the results?
The pathology of your SCB will determine if the suspicious lesion contained any abnormal cells, such as cancer. Pathology results can take any number of days, all depending on the which day of the week and where the biopsy was taken, whether path results are interpreted in-house or outsourced, and whether the department in question is multi-disciplinary or dedicated solely to breast cancer. At the Pink Lotus Breast Center, which I oversee as Medical Director, we have developed a unique process that allows patients to typically receive their results by the next business day, which can help with keeping anxiety at bay.